rubix_cube.cube module¶
Rubix Cube class data-structure Module
Module Description¶
Collection of methods that define the main Rubix Cube class data
structure and how it is interacted with by other modules.
Note
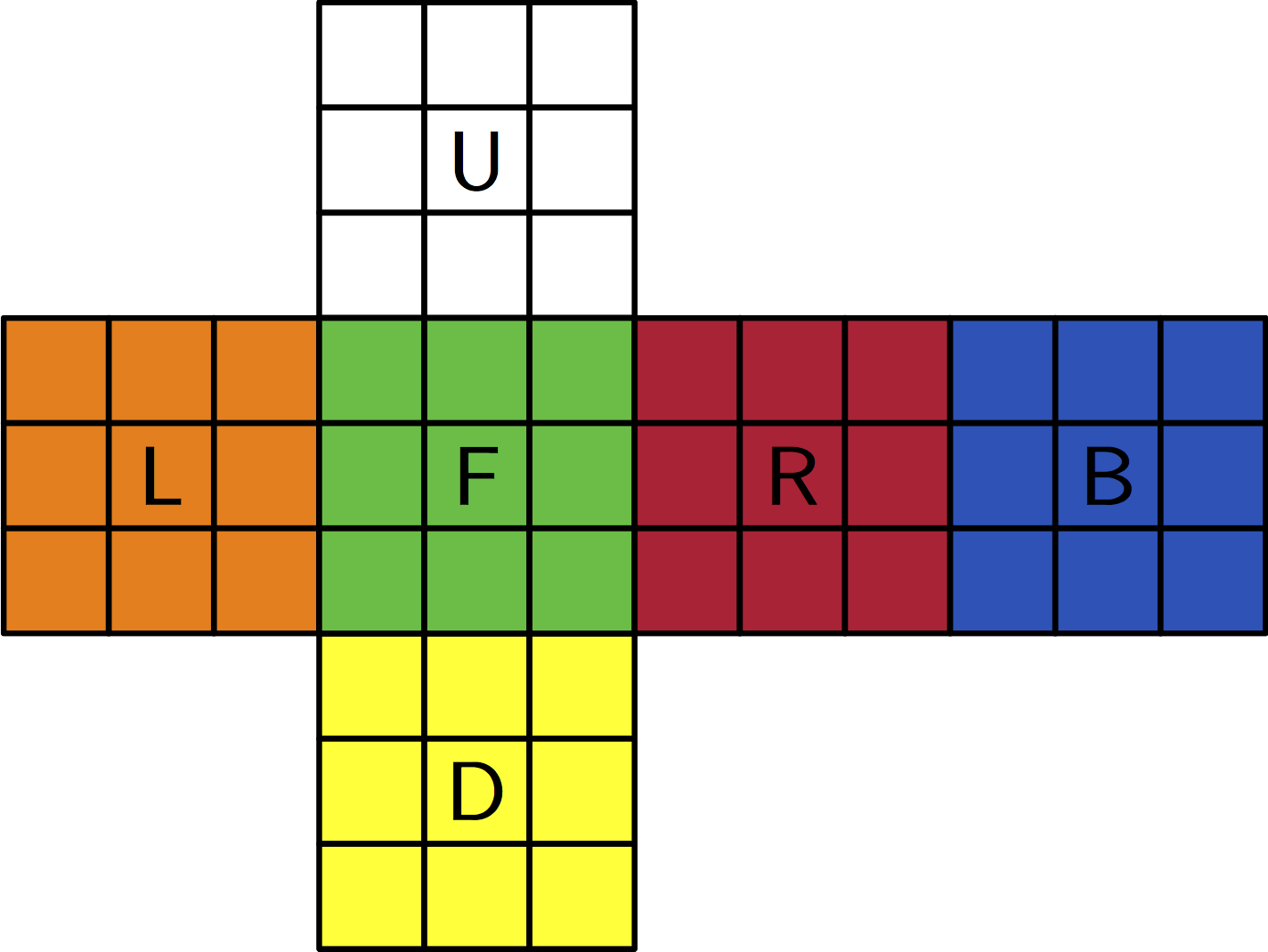
Using Western Color Scheme as default Rubix Cube coloring scheme.
Module Contents¶
Rubix Cubeclass that is capable of being parameterized with a custom set of 6 unique colors (Default Color Scheme) and can invoke the following moves.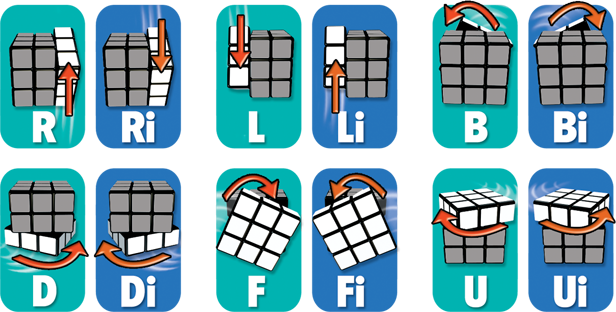
6 cube face rotations both clock-wise and counter-clockwise (inverse) are considered to be the standard move-set. (How to Solve )¶
Todo
Need to finish implementing the
get_num_solved_rings.
-
class
rubix_cube.cube.Cube(colors: Dict[str, int] = None, faces: Dict[str, numpy.array] = None)[source]¶ Bases:
objectData structure for representing a 3x3x3 rubix-cube.
-
__faces¶ Dictionary of
numpy arraysthat define the rendering of theCube’s tile configuration.- Type
Dict[str,np.ndarray]
-
DEFAULT_BACK_COLOR= '#0045ad'¶
-
DEFAULT_BACK_FACE= array([['#0045ad', '#0045ad', '#0045ad'], ['#0045ad', '#0045ad', '#0045ad'], ['#0045ad', '#0045ad', '#0045ad']], dtype='<U7')¶
-
DEFAULT_DOWN_COLOR= '#ffd500'¶
-
DEFAULT_DOWN_FACE= array([['#ffd500', '#ffd500', '#ffd500'], ['#ffd500', '#ffd500', '#ffd500'], ['#ffd500', '#ffd500', '#ffd500']], dtype='<U7')¶
-
DEFAULT_FACES= {'BACK_FACE': array([['#0045ad', '#0045ad', '#0045ad'], ['#0045ad', '#0045ad', '#0045ad'], ['#0045ad', '#0045ad', '#0045ad']], dtype='<U7'), 'DOWN_FACE': array([['#ffd500', '#ffd500', '#ffd500'], ['#ffd500', '#ffd500', '#ffd500'], ['#ffd500', '#ffd500', '#ffd500']], dtype='<U7'), 'FRONT_FACE': array([['#009b48', '#009b48', '#009b48'], ['#009b48', '#009b48', '#009b48'], ['#009b48', '#009b48', '#009b48']], dtype='<U7'), 'LEFT_FACE': array([['#ff5900', '#ff5900', '#ff5900'], ['#ff5900', '#ff5900', '#ff5900'], ['#ff5900', '#ff5900', '#ff5900']], dtype='<U7'), 'RIGHT_FACE': array([['#b90000', '#b90000', '#b90000'], ['#b90000', '#b90000', '#b90000'], ['#b90000', '#b90000', '#b90000']], dtype='<U7'), 'UP_FACE': array([['#ffffff', '#ffffff', '#ffffff'], ['#ffffff', '#ffffff', '#ffffff'], ['#ffffff', '#ffffff', '#ffffff']], dtype='<U7')}¶
-
DEFAULT_FACE_COLORS= {'BACK_COLOR': '#0045ad', 'DOWN_COLOR': '#ffd500', 'FRONT_COLOR': '#009b48', 'LEFT_COLOR': '#ff5900', 'RIGHT_COLOR': '#b90000', 'UP_COLOR': '#ffffff'}¶
-
DEFAULT_FRONT_COLOR= '#009b48'¶
-
DEFAULT_FRONT_FACE= array([['#009b48', '#009b48', '#009b48'], ['#009b48', '#009b48', '#009b48'], ['#009b48', '#009b48', '#009b48']], dtype='<U7')¶
-
DEFAULT_LEFT_COLOR= '#ff5900'¶
-
DEFAULT_LEFT_FACE= array([['#ff5900', '#ff5900', '#ff5900'], ['#ff5900', '#ff5900', '#ff5900'], ['#ff5900', '#ff5900', '#ff5900']], dtype='<U7')¶
-
DEFAULT_RIGHT_COLOR= '#b90000'¶
-
DEFAULT_RIGHT_FACE= array([['#b90000', '#b90000', '#b90000'], ['#b90000', '#b90000', '#b90000'], ['#b90000', '#b90000', '#b90000']], dtype='<U7')¶
-
DEFAULT_UP_COLOR= '#ffffff'¶
-
DEFAULT_UP_FACE= array([['#ffffff', '#ffffff', '#ffffff'], ['#ffffff', '#ffffff', '#ffffff'], ['#ffffff', '#ffffff', '#ffffff']], dtype='<U7')¶
-
__eq__(other) → bool[source]¶ Tests if the
Rubix Cubefaces are exactly identical between the two objects.- Parameters
other (TYPE) – Description
- Returns
Description
- Return type
-
__init__(colors: Dict[str, int] = None, faces: Dict[str, numpy.array] = None)[source]¶ Cubeclass constructor.- Parameters
colors (Dict[str,str], optional) –
Dictionary of color HEX strings. Default value is
Nonewhich will create a cube with default colorsDEFAULT_FACE_COLORS.Requiredcolorsdictionary keys.¶1 2 3 4 5 6 7
colors = {'UP_COLOR' : ..., 'DOWN_COLOR' : ..., 'FRONT_COLOR' : ..., 'BACK_COLOR' : ..., 'LEFT_COLOR' : ..., 'RIGHT_COLOR' : ... }
All colors passed as values must return
Truewhen examined bymatplotlib.colors.is_color_like().faces (Dict[str,np.array], optional) –
Dictionary of face names to 3x3 arrays of the the tile face values. Default value is
Nonewhich will create a solved cube with default colors.Requiredfacesdictionary keys.¶1 2 3 4 5 6 7
faces = {'UP_FACE' : ..., 'DOWN_FACE' : ..., 'FRONT_FACE' : ..., 'BACK_FACE' : ..., 'LEFT_FACE' : ..., 'RIGHT_FACE' : ... }
All faces passed as value must be 3x3
numpy arrayswith each element returningTruewhen examined bymatplotlib.colors.is_color_like().
-
__mod__(other) → bool[source]¶ Tests if the
Rubix Cubefaces are exactly identical between the two objects after re-orientation. Essentially are the cubes identical after rotation?- Parameters
other (TYPE) – Description
- Returns
- Return type
-
__ne__(other) → bool[source]¶ Tests if the
Rubix Cubefaces areNOTexactly identical between the two objects.- Parameters
other (TYPE) – Description
- Returns
Description
- Return type
-
property
colors¶ Can only be set to be a dictionary with 6 unique color string values that all return
Truewhen examined bymatplotlib.colors.is_color_like().Requiredcolorsdictionary keys.¶1 2 3 4 5 6 7
colors = {'UP_COLOR' : ..., 'DOWN_COLOR' : ..., 'FRONT_COLOR' : ..., 'BACK_COLOR' : ..., 'LEFT_COLOR' : ..., 'RIGHT_COLOR' : ... }
-
property
faces¶ Can only be set to be a dictionary of 6 strings mapped to the faces of a Rubix Cube. Each value must be a 3x3
numpy arrayof values all of which are valid colors that can be found within thecolorsattribute.Requiredfacesdictionary keys.¶1 2 3 4 5 6 7
faces = {'UP_FACE' : ..., 'DOWN_FACE' : ..., 'FRONT_FACE' : ..., 'BACK_FACE' : ..., 'LEFT_FACE' : ..., 'RIGHT_FACE' : ... }
-
get_num_matching_adjacent_tiles() → int[source]¶ Counts the number of tiles on the
Cubethat are adjacent and have the same color values. Uses successive calls toget_num_matching_adjacent_tiles_face()for every face.
-
get_num_matching_adjacent_tiles_face(face: numpy.ndarray) → int[source]¶ Counts the number of tiles on the current face that are adjacent and have the same color values.
-
get_num_solved_faces() → int[source]¶ Counts the number of solved faces by examining each one using
is_solved_face()if the currently initializedCubeis_well_formed(), 0 otherwise.
-
is_solved() → bool[source]¶ Calls
get_num_solved_faces()to check if all faces of theCubeare solved.- Returns
Value representing if all faces are solved completely.
- Return type
Checks to see if the number of solved faces is 6.¶1
return (self.get_num_solved_faces() == 6)
-
is_solved_face(face: numpy.ndarray) → bool[source]¶ Checks if the provided array could be a valid face on the currently initialized
Cube.- Parameters
face (np.ndarray) – Array to be tested for being solved in the context of the current
Cube.- Returns
Trueif faces is solved 3 x 3 array of valid colors as defined by current instance’scolorsattribute,Falseotherwise.
A solvedfacereturnsTruewhen examined byis_valid_face()and only contains 1 unique value.¶1
return len(np.unique(face) == 1)
-
is_valid_face(face: numpy.ndarray) → bool[source]¶ Checks if the provided array could be a valid face on the currently initialized
Cube.
-
is_well_formed() → bool[source]¶ Quality control method to ensure class has been properly initialized by examining all
facesvia the quality control methodis_valid_face().- Returns
Trueif all faces are 3 x 3 arrays of valid colors as defined bymatplotlib.colors.is_color_like(),Falseotherwise.
-
to_json_safe_dict() → Dict[source]¶ Constructs a JSON-safe dictionary for saving
Cubestate to JSON file.- Returns
json_dict - JSON-safe dictionary with faces attribute dict values converted from
numpy.ndarraytolist.- Return type
Dict
-